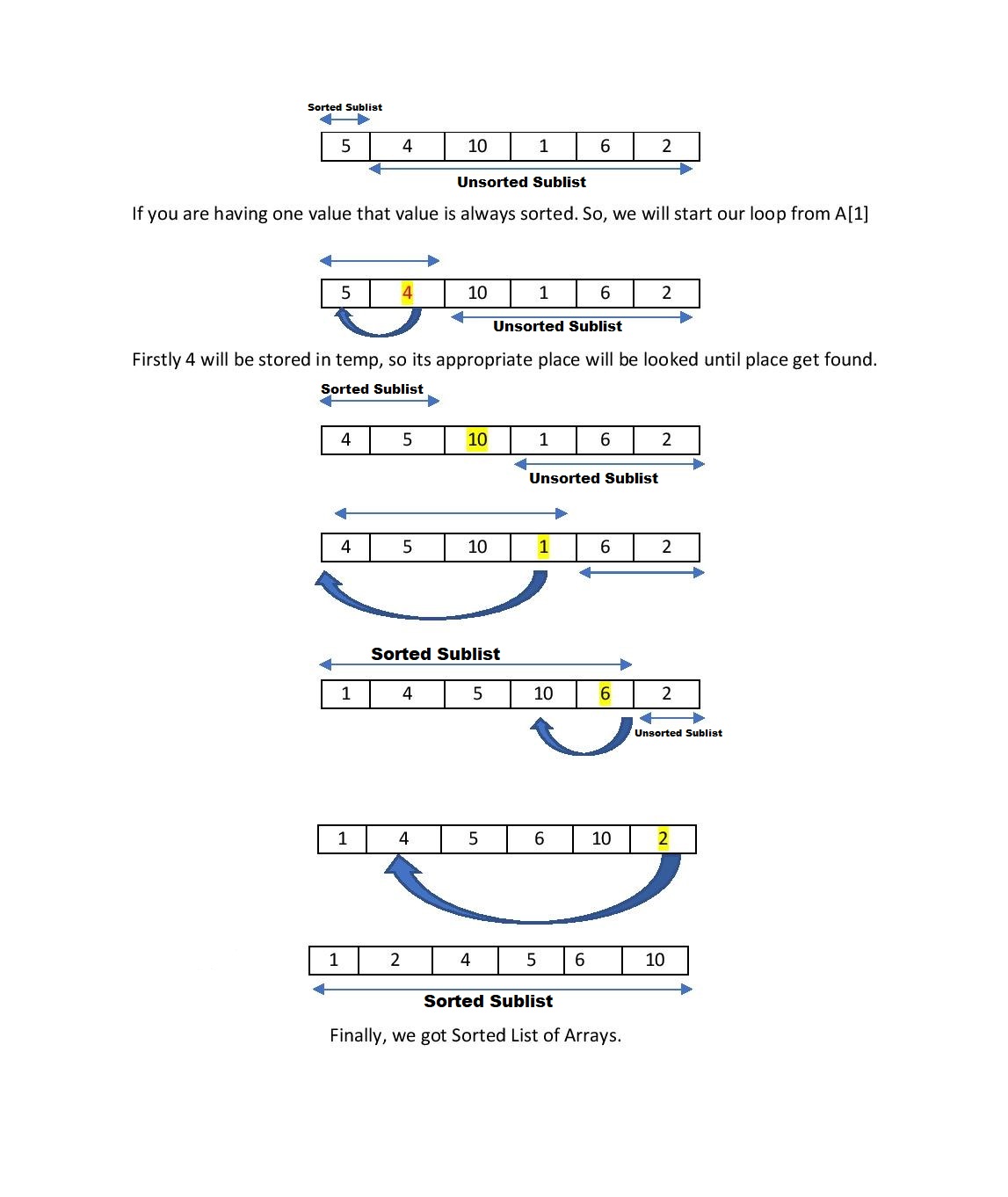
Insertion Sort Algorithm: In this technique, given array is divided into two parts.
1. Sorted Sublist (array)
2. Unsorted Sublist (array)
Steps to follow During Insertion Sort Algorithm:
- Firstly, we are going to pick one value from the unsorted sub list let us say we store that value in temp variable.
- Then, we are going to find out the appropriate place for that value (say temp) in sorted sub list and push all bigger elements than temp one place ahead.
- After finding, we will insert temp in Sorted Sub list in its correct place.
Two loops will be required, one for increment of i and other for
decrement of j (until j >= 0).
Remember: j is always intitialized one step behind than i.
Code:
public class InsertionSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[] = { 100, 23, 1, 0, 45, 11, 78 };
int n = arr.length;
// calling insertionSort method which will make the array sorted
insertionSort(arr, n);
System.out.print("Sorted Arrays by using Insertion Sort Method: ");
printSortedArray(arr, n); // for displaying the array
}
private static void insertionSort(int[] arr, int n) {
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int temp;
temp = arr[i];
int j; // j should be always one place behind i
for (j = i - 1; j >= 0 && arr[j] > temp; j--) {
arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
}
arr[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
private static void printSortedArray(int[] arr, int n) {
n = arr.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
Output:
Sorted Arrays by using Insertion Sort Method: 0 1 11 23 45 78 100
Complexity Analysis:
Time Complexity:
Worst Case: When array is given in descending order then time complexity isO(N2).
Best Case: When array is in ascending order or sorted, in that case time
complexity will be O(N).
Space Complexity: O(1), we have not used any extra space.